Ethylene, propylene, and diene monomers are the components of EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer), a synthetic rubber. Its single bond, chemically-saturated molecular structure gives it a very strong resistance to the elements. This is due to the fact that, unlike double-bonded rubbers, its molecular structure cannot be disrupted by ozone or UV rays. Read More…
RD Rubber Technology Corp is an ISO 9001:2015 / AS9100:2016 certified and ITAR registered company. We offer compression, transfer, injection and Liquid Injection molding, rubber to metal bonding, engineering support, tooling design, machining and more. Our customers rely on us to give them the best possible production solutions for rubber molding. From aerospace to medical, food processing to military applications we build trust by being responsive to your needs.

If you have a need custom rubber molding for products with a fast turnaround, Britech Industries is the company you need to call. We do molded, extruded and die cut rubber – of various products and in the colors and compounds you need.

With more than a century of manufacturing experience, Pierce-Roberts Rubber Co. is your source for custom molded rubber products.
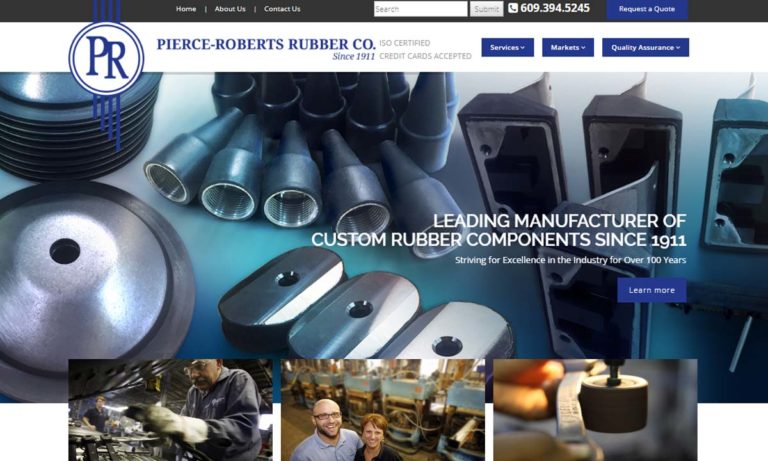
Rubber molding is what we do best. We believe in offering our very best to all customers no matter how large or small. For over 65 years we have pushed the boundaries of what we do and continue to improve our products and customer service every day.
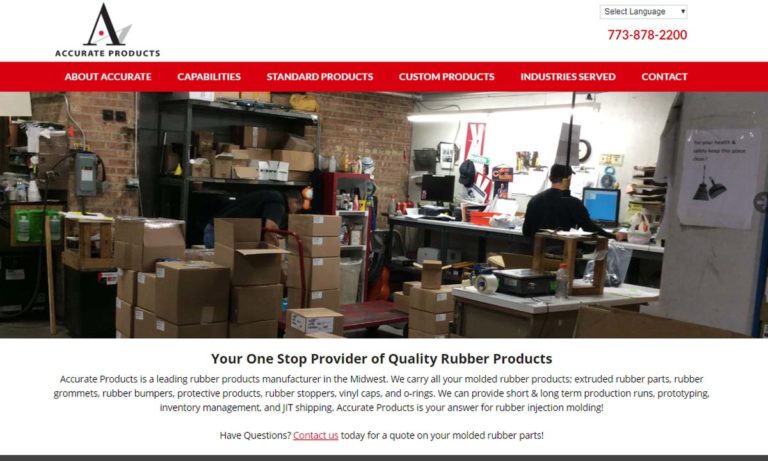
REDCO Rubber Engineering & Development is your complete source for rubber molding products, including rubber rollers, die-cut gaskets, and custom rubber products to suit your application.
All your typical molded rubber parts & more! Our custom rubber molding expertise includes mold conversion, non-conductive parts, injection molding, compression molding, transfer molding, die cutting & extrusions, plus cryogenic deflashing, trimming and curing. Low to medium volumes on time & budget!

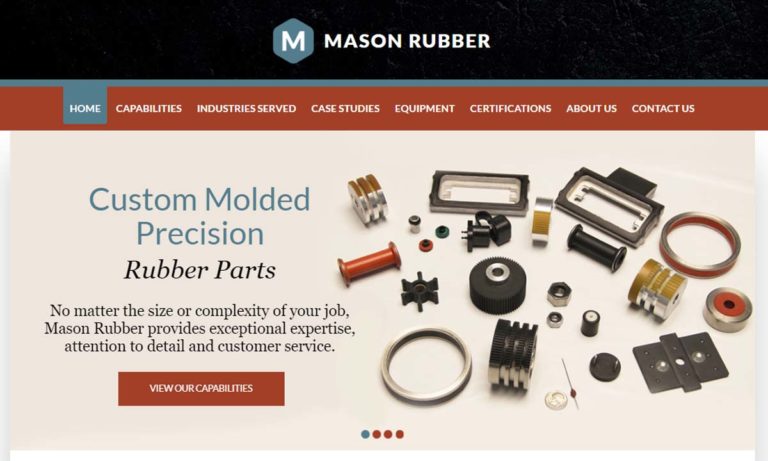
Mason Rubber is a full-service organization assisting in the designing or reverse engineering of custom product to fulfill your production requirements.
Kent Rubber Supply leverages our experience, innovation and continuous development to ensure our customers get the best products. We specialize in small to large batch production runs of molded rubber parts, allowing us to offer ultimate customization when it comes to a wide variety of specs. Our products vary in shapes, sizes and wall thicknesses in materials such as PVC and urethane. Both domestic and offshore services are available.

Spring-Fast Grommets with fusion bonded nylon & a polymer cushion prevent wire chafe & give you best in class performance, 49% install savings & a 9.5x efficiency improvement. The nylon clad metal substrate snaps on with finger pressure & self locks - eliminating adhesives & the old slow & costly gluing process. It is used widely used in across the OEM & contract manufacture sectors. ISO 9001:2015 & AS 9100-D. Collaborative product customization available. Request free samples on site.
National Rubber was founded in 1997 with the values of variety, consistency, quality, open communication, and timely delivery at its core. Today, we stay true to these values by taking each one of your specifications into consideration, and working with you through every step of the manufacturing process. Call us today for more information!

Jet Rubber Company, employee-owned, offers custom molded rubber and rubber to metal components. They offer rubber molding in a wide array of standard rubber products as well as custom options for those more complex and difficult jobs.

More EPDM Rubber Molding Companies
EPDM rubber (ethylene propylene diene monomer rubber) is a highly versatile synthetic rubber material, prized for its exceptional durability, flexibility, and superior resistance to environmental factors. As one of the most popular types of synthetic elastomers, EPDM is engineered to withstand harsh outdoor conditions, temperature extremes, and aggressive chemicals, making it a go-to choice for demanding applications in various industries. If you’re searching for “EPDM rubber applications,” “EPDM molding process,” or “best EPDM manufacturer,” this comprehensive guide will help you understand the benefits, uses, and decision factors for sourcing quality EPDM products.
Commonly used in the automotive industry for radiator and cooling system hoses, window and door weatherstripping, and as a sealing component, EPDM’s unique polymer structure provides outstanding performance advantages over natural rubber. While natural rubber can become brittle and lose elasticity with temperature fluctuations, EPDM synthetic rubber maintains its flexibility, resilience, and sealing properties for decades, even under rigorous thermal cycling. This makes it especially valuable in environments subject to sunlight, ozone, and weathering. EPDM is found in cold storage facilities, non-slip playground surfacing, waterproofing systems, roofing membranes, and countless other high-performance settings.

What Is EPDM Rubber? Exploring Its Chemistry and Unique Properties
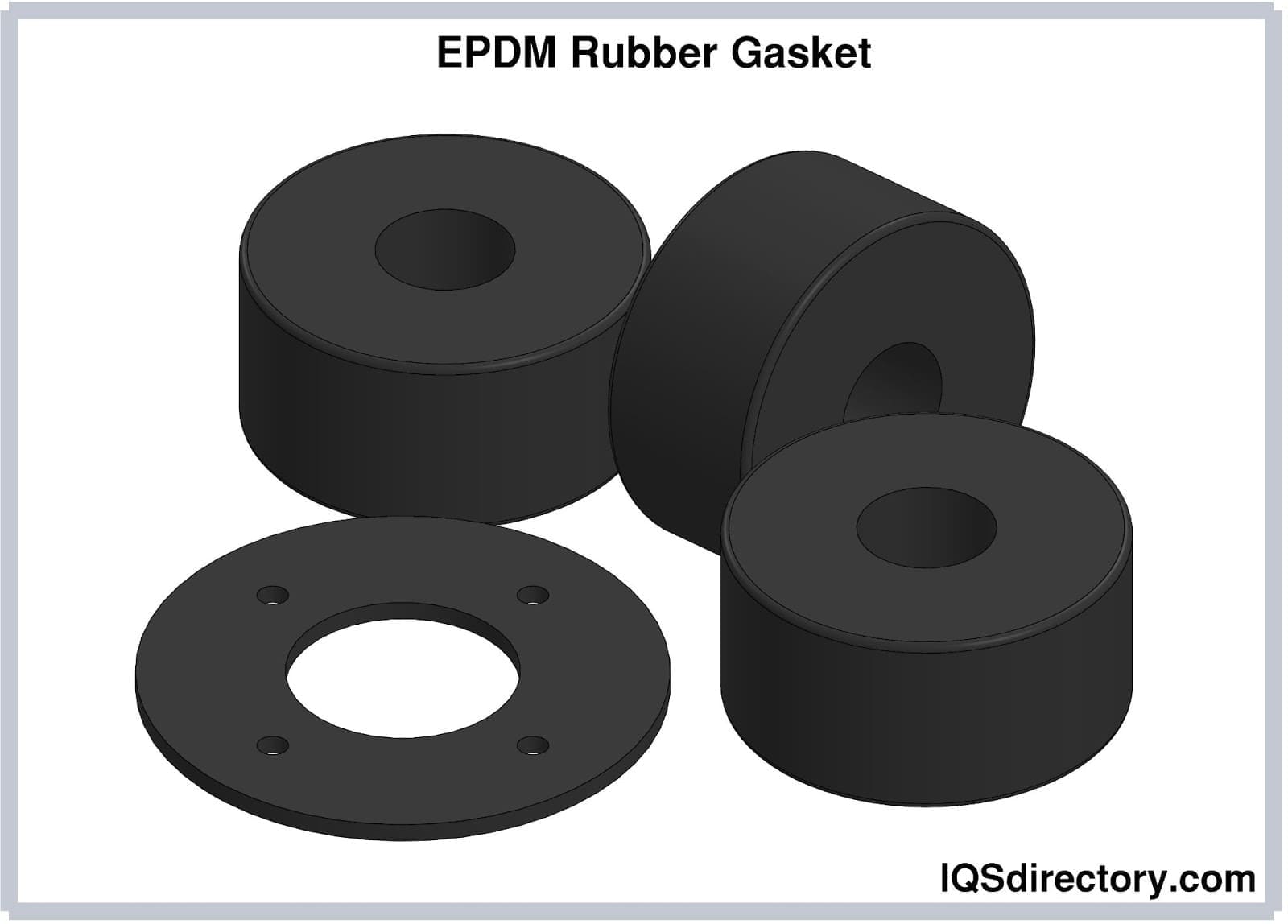
EPDM (ethylene propylene diene monomer) is a synthetic elastomer produced by polymerizing ethylene, propylene, and a small amount of non-conjugated diene monomer. The result is a rubber compound with a saturated backbone, which offers remarkable resistance to heat, oxidation, ozone, and ultraviolet (UV) light. This unique molecular structure makes EPDM rubber ideal for outdoor and industrial applications where other rubbers may degrade or fail. EPDM is also highly resistant to steam, water, polar substances, and a wide variety of chemicals, making it a preferred material for sealing, gasketing, and waterproofing solutions.
Key properties of EPDM rubber include:
- Excellent weatherability: Superior resistance to ozone, UV rays, and extreme weather conditions.
- Wide temperature range: Functional from -40°C up to +150°C (-40°F to +302°F), depending on formulation.
- Superb electrical insulation: Low electrical conductivity, ideal for electrical and electronic applications.
- Outstanding flexibility and elasticity: Remains pliable and retains sealing ability even after years of exposure.
- Chemical resistance: Withstands acids, alkalis, phosphate esters, and many polar fluids.
- Low compression set: Maintains shape and performance under pressure and repeated deformation.
- Non-toxic and environmentally friendly options are available for food-grade and potable water applications.
EPDM Molding Process: How Are EPDM Rubber Parts Manufactured?
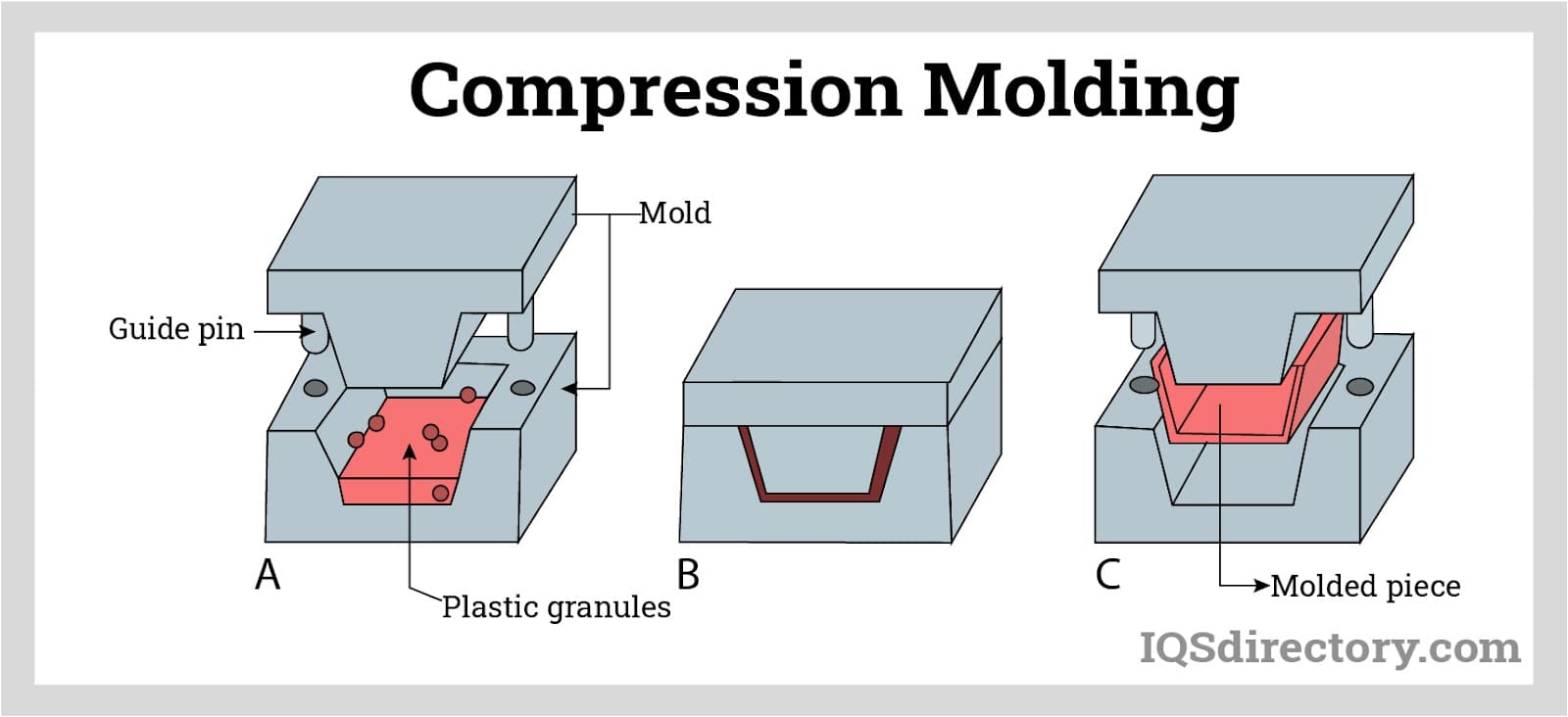
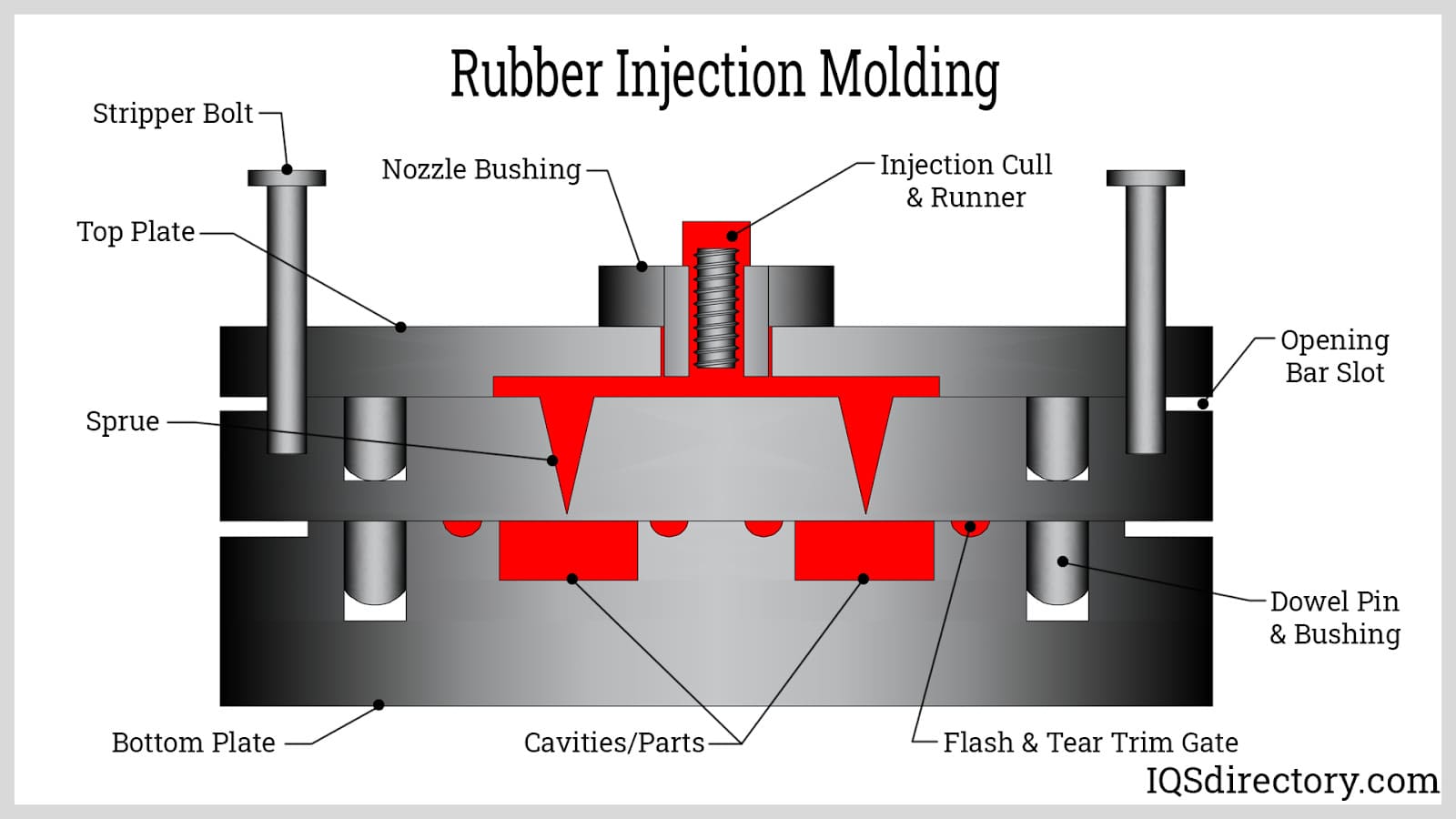
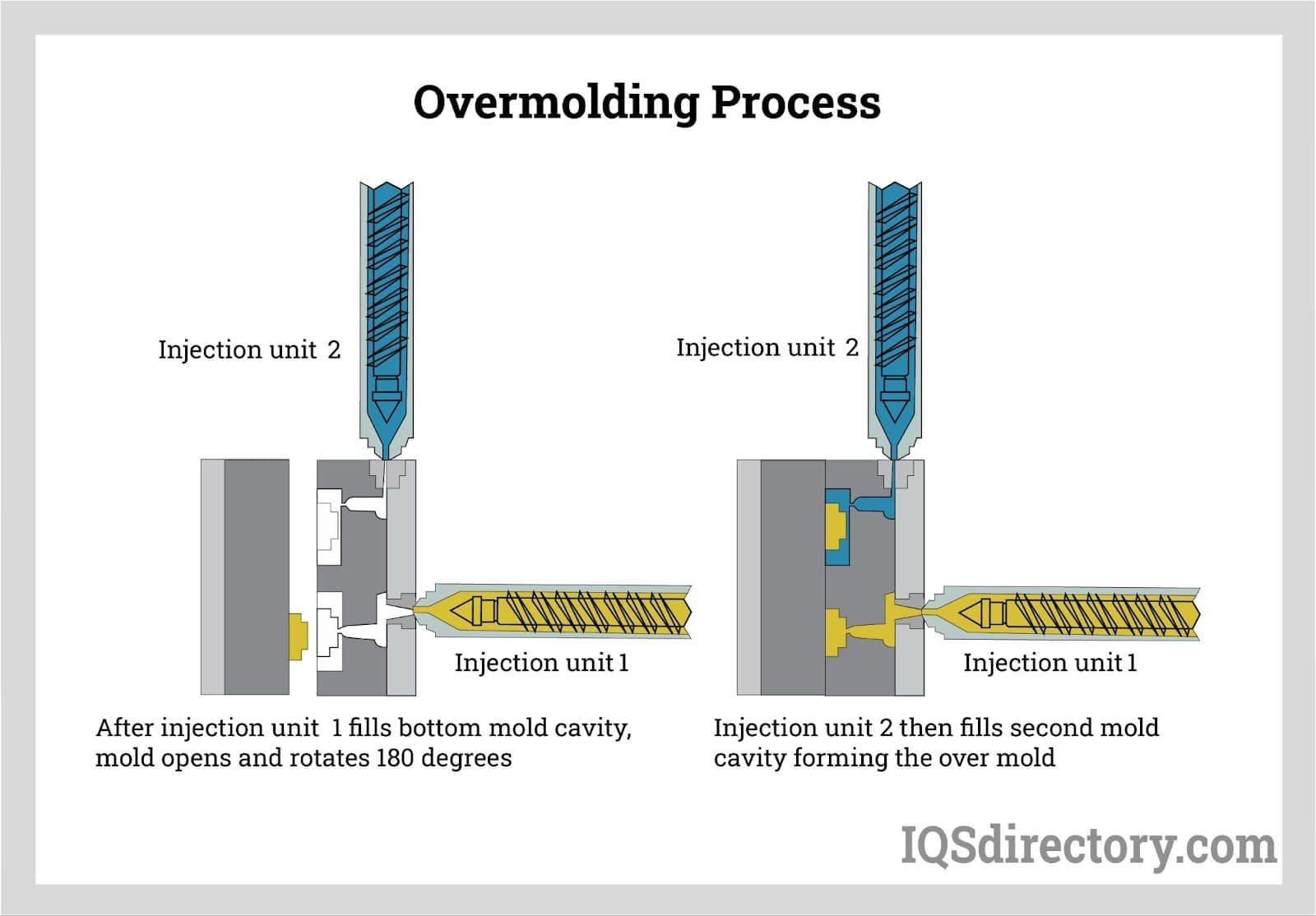
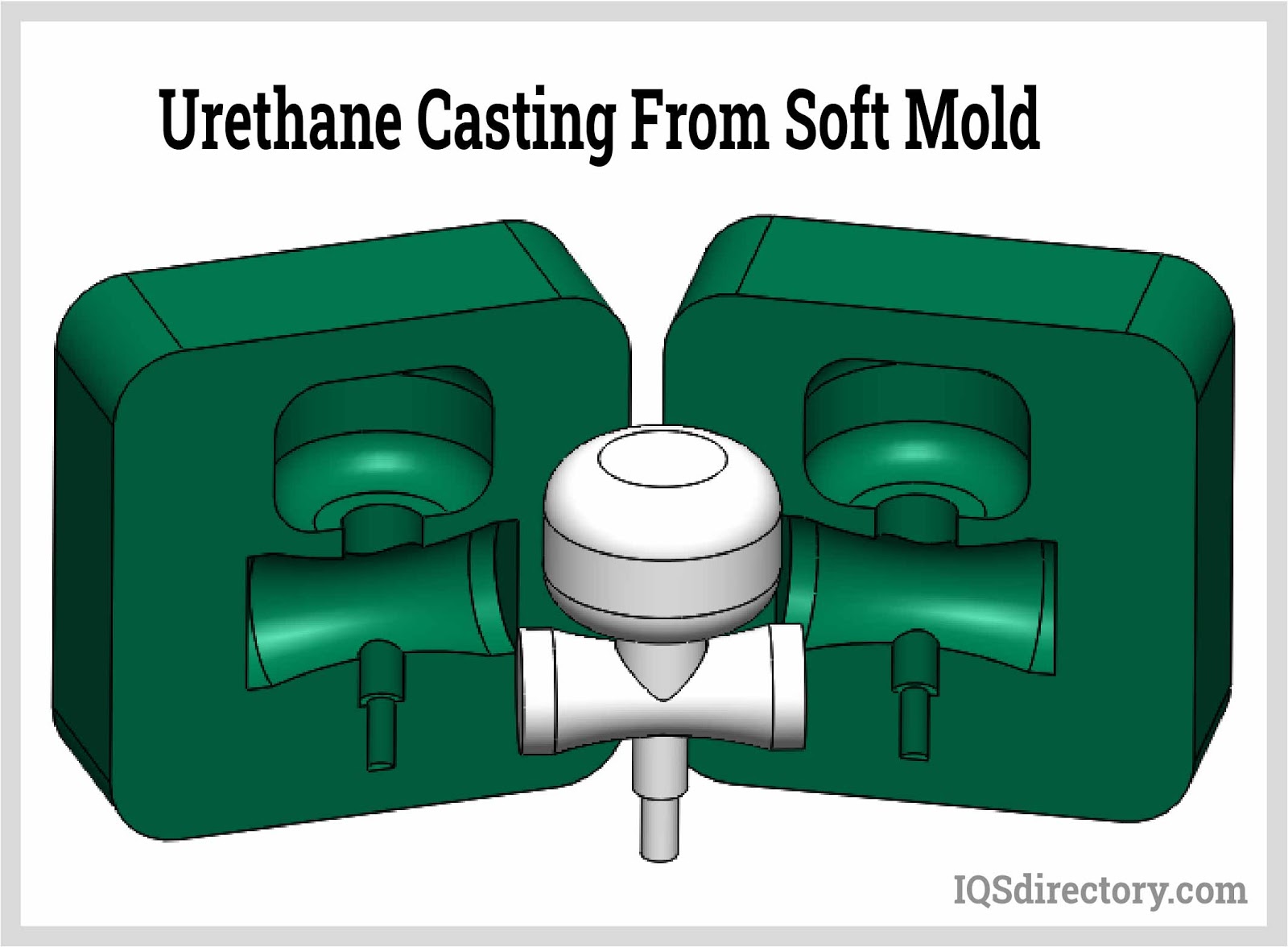
Understanding the EPDM molding process is critical for buyers and engineers seeking custom rubber components. EPDM parts are most commonly produced using advanced injection molding, compression molding, and transfer molding techniques. Here’s an overview of the typical injection molding process for EPDM:
The process begins by closing the mold and introducing pre-heated EPDM rubber into the open mold cavity. For injection molding, a carefully measured amount of EPDM compound is cut into strips and fed through a heated screw and barrel system, which plasticizes the material before injection.
As the mold cavity fills, strategically placed vents allow displaced air to escape, preventing air entrapment, voids, or surface imperfections in the finished part. Unlike plastics, EPDM rubber compounds require significantly higher molding pressures and temperatures—this ensures full cure and optimal cross-linking of the polymer chains. The cycle time (the interval needed for the rubber to fully vulcanize and cure) varies depending on part geometry, thickness, and specific compound formulation.
Once the curing cycle is complete, the mold opens, and finished EPDM parts are either manually removed or ejected automatically. The cycle then repeats for efficient, high-volume production. EPDM rubber molding can accommodate intricate shapes, tight tolerance requirements, and a wide range of durometers (hardness), making it suitable for everything from soft gaskets to rigid seals and structural components.

EPDM Molding Techniques: Injection, Compression, and Transfer Molding
EPDM rubber can be shaped using several molding methods, each offering unique advantages for different use cases:
- Injection Molding: Ideal for high-volume, precision parts such as O-rings, gaskets, and automotive weather seals. This automated process delivers consistent quality and tight dimensional tolerances.
- Compression Molding: Suited for large, thick, or custom-shaped parts where high pressure is needed to flow the material into the mold. Often used for grommets, seals, and insulating pads.
- Transfer Molding: Combines elements of both injection and compression molding, allowing for complex part geometries, insert molding, and multiple cavity production. Ideal for medium-volume production and rubber-to-metal bonded parts.
If you’re evaluating which EPDM molding method is best for your project, consider factors like production volume, part complexity, required material properties, and cost targets.
Advantages of EPDM Molding: Why Choose EPDM Rubber?
EPDM stands out among synthetic rubbers for its broad performance envelope and cost-effectiveness. Here are the top benefits of using EPDM rubber in manufacturing and product design:
- Exceptional resistance to UV, ozone, and weathering: EPDM’s saturated polymer backbone provides unmatched durability outdoors, even after years of sun exposure and harsh weather.
- Excellent chemical resistance: EPDM resists attack from acids, alkalis, and polar solvents, making it safe for use in industrial, automotive, and water system applications.
- Superior temperature stability: Maintains flexibility and sealing efficiency in both extremely hot and frigid environments.
- Water, steam, and moisture resistance: Ideal for waterproofing membranes, gaskets, and HVAC seals exposed to condensation and humidity.
- Electrical insulation properties: Low conductivity enables use in wire and cable insulation, grommets, and electrical enclosures.
- Versatility across industries: From roofing and construction to automotive and industrial machinery, EPDM adapts to diverse application needs.
- Cost-effective compared to silicone: EPDM delivers many of the same performance advantages at a lower price point, supporting large-scale manufacturing and OEM supply chains.
- Eco-friendly and energy efficient: White EPDM roofing membranes reflect UV rays, reduce cooling costs, and are compatible with green roofs and solar panels. The material’s lightweight nature minimizes installation effort and energy usage, and EPDM is fully recyclable.
- Longevity and reduced maintenance: EPDM’s resistance to aging and physical wear reduces replacement frequency, lowers total cost of ownership, and supports sustainability goals.

Common Applications of EPDM Rubber: Where Is EPDM Used?
EPDM is a preferred material in countless industries thanks to its impressive performance profile. Here are some of the most common and emerging EPDM rubber applications:
- Automotive Industry: EPDM is widely used for weatherstripping, window and door seals, cooling system hoses, brake system components, and wire/cable harnesses. It’s also compounded into bumper strips, fender extensions, and vibration dampening mounts—helping vehicles withstand temperature swings, road salt, ozone, and moisture.
- Industrial and Manufacturing: EPDM is found in O-rings, gaskets, diaphragms, hoses, belts, and grommets for water systems, pumps, and machinery. Its electrical insulation properties make it essential for wire and cable connectors, electrical enclosures, and power generation equipment.
- Construction and Roofing: EPDM’s waterproofing, insulation, and weatherproofing properties make it a leading material for roofing membranes, expansion joints, bituminous roof coatings, garage door seals, pool liners, and tank liners. It’s also used in curtain wall gaskets and sealing solutions for energy-efficient buildings and RV roofs.
- HVAC Systems: EPDM’s ability to withstand temperature changes and resist condensation makes it ideal for insulation tubing, seals, gaskets, and grommets in air conditioning and heating units.
- Pond and Water Feature Liners: EPDM liner membranes are used to create durable, leak-proof barriers for backyard ponds, fountains, and water gardens. These liners are highly flexible, easy to install, and offer a lifespan of 30 years or more. EPDM is inert, bleach-resistant, and safe for aquatic life, birds, plants, and pets.
- Water and Biogas Tank Liners: The dense molecular structure of EPDM rubber prevents moisture and vapor transmission, making it ideal for water tanks, biogas storage, and chemical containment. Its non-shrinking, crack-resistant nature ensures long-term performance in harsh environments.
- Playground, Sports, and Safety Surfaces: EPDM granules are used in poured-in-place rubber safety surfacing for playgrounds, running tracks, and sports facilities. The material’s shock absorption, slip resistance, and vibrant color options support safe and attractive recreational surfaces.
- Solar and Green Roofing: EPDM’s UV resistance and compatibility with solar panel installations make it a top choice for sustainable roofing systems and green building projects.
- Marine and Aerospace: EPDM seals and gaskets are valued for their ability to resist saltwater, extreme temperatures, and vibration, protecting critical systems in ships, aircraft, and aerospace equipment.
Looking for a specific EPDM product or custom-molded component?
Ask questions like: “What is the best EPDM compound for outdoor sealing?” “How do I choose between EPDM and silicone rubber?” or “Where can I find a certified EPDM gasket manufacturer?” Our team can help you select the right material and production process for your unique application.
EPDM vs. Other Elastomers: How Does EPDM Compare?
When evaluating elastomers for your application, it’s important to compare EPDM with other popular materials such as natural rubber, neoprene, nitrile (NBR), and silicone rubber. Here’s how EPDM stacks up:
- EPDM vs. Natural Rubber: EPDM offers superior weather, ozone, and chemical resistance, as well as a wider temperature range. Natural rubber is more suitable for dynamic, high-flex applications at room temperature, but degrades faster outdoors.
- EPDM vs. Neoprene: While both offer good weather resistance, EPDM excels in UV and ozone resistance, whereas neoprene is preferred for oil and fuel contact. EPDM is not recommended for use with petroleum oils and hydrocarbons.
- EPDM vs. Nitrile (NBR): Nitrile is best for oil and fuel resistance, while EPDM is superior for water, steam, and polar chemical environments.
- EPDM vs. Silicone Rubber: Silicone withstands higher temperatures and is suitable for food and medical uses, but is more expensive. EPDM provides similar weatherability at a lower cost, making it ideal for large-scale commercial and industrial applications.
How to Select the Right EPDM Compound and Manufacturer
Choosing the right EPDM rubber compound and manufacturing partner is crucial for ensuring optimal performance, longevity, and value in your application. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you make informed sourcing decisions:
- Define your application requirements: Consider temperature range, exposure to chemicals, UV, or ozone, mechanical stress, and compliance (such as NSF, FDA, or ASTM standards).
- Determine the ideal molding process: Based on part complexity, production volume, and budget, select between injection, compression, or transfer molding.
- Research and compare EPDM manufacturers: Look for suppliers with a proven track record, quality certifications, and experience in your industry. Evaluate their capabilities in custom compounding, prototyping, and volume production.
- Request samples and technical data: Ask for material datasheets, product samples, and case studies to validate performance in your intended use environment.
- Request quotations and lead times: Obtain detailed pricing, minimum order quantities, and delivery timelines. Consider after-sales support, warranty terms, and technical assistance.
To ensure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing EPDM from an EPDM manufacturer, it’s important to compare at least 4 companies using our list of EPDM manufacturers. Each EPDM manufacturer has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities, and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each EPDM company website using our proprietary website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple EPDM companies with the same form.
Frequently Asked Questions About EPDM Rubber
- What is EPDM rubber used for? Explore common and innovative applications for EPDM in automotive, construction, industrial, HVAC, roofing, and more.
- How does EPDM compare to other synthetic rubbers? Discover the advantages and limitations of EPDM relative to neoprene, nitrile, silicone, and natural rubber.
- Is EPDM safe for potable water or food contact? EPDM compounds can be formulated to meet NSF/ANSI and FDA standards for safe use in drinking water and food processing applications.
- Can EPDM be recycled or considered environmentally friendly? Yes, EPDM is recyclable and available in eco-friendly formulations for sustainable building and manufacturing projects.
- How long does EPDM rubber last? Properly installed EPDM products can last 20–50 years or more, depending on environmental exposure and maintenance.
- What are the limitations of EPDM? EPDM is not suitable for continuous exposure to petroleum oils, hydrocarbons, or concentrated acids, but excels in most weather, water, and polar chemical environments.
- Can EPDM rubber be colored or customized? Absolutely. EPDM can be compounded in a broad range of colors and hardness levels, supporting custom branding and functional requirements.
Get Started: Request a Quote for Custom EPDM Rubber Parts
Ready to source high-quality EPDM rubber parts or need expert guidance on material selection and design? Contact our vetted EPDM manufacturers to discuss your project, request samples, or obtain a fast, competitive quote. Whether you need custom-molded EPDM gaskets, seals, O-rings, or specialized components, our network connects you with industry-leading suppliers offering advanced compounding, precision molding, and reliable delivery.
Still have questions? Search for answers such as: “Which EPDM grade is best for outdoor UV protection?” “How do I ensure my EPDM seals are compliant with industry standards?” “What is the typical lead time for custom EPDM molding?” Our experts are here to help you every step of the way.
Experience the long-term performance, cost savings, and design flexibility that EPDM rubber offers across today’s most demanding industries. Make the smart choice for your next project—and let us help you find the perfect EPDM solution for your needs.

















 Rubber Extrusions
Rubber Extrusions Rubber Molding
Rubber Molding Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to Metal Bonding Rubber Tubing
Rubber Tubing Vibration Absorbers
Vibration Absorbers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services